Aworker Introduction
A Web-interoperable JavaScript runtime that provides Web API standards, suitable for business logic deployment that does not directly depend on system interfaces. Aworker implements a specification similar to Service Worker API, providing a basic Request-Response service API.
Because it provides a higher-level and abstract definition than the API of Node.js, it will not leak the underlying state of the system. Aworker achieves faster horizontal and vertical expansion through Startup Snapshot and WarmFork capabilities, can be started in milliseconds and also handle traffic with higher elastic efficiency.
Warmfork
It is well known that the fork(2) system call has several advantages:
- The new process can inherit the current state of the parent process without initializing it from main();
- The pcb, stack, memory page, and page table are all pure memory copy, so the process creation is fast (<1ms);
- CopyOnWrite, the new process can inherit the static page table of the parent process, which can save system memory;
For Node.js, because it cannot hold all multi-threaded states (such as locks, semaphores, etc.) in the main thread, it is very difficult to fork Node.js. The multi-threaded design of Node.js is mainly From libuv library and V8 Platform Worker threads:
- Because some I/O operations have synchronous calls, such as dns, file reading and writing, etc., libuv uses IO threads to convert synchronous operations into asynchronous operations;
- The default configuration of Node.js V8 is multi-threaded GC, Background Compilation/Optimization.
The single-process multi-threading model of Node.js can be represented by the following diagram:
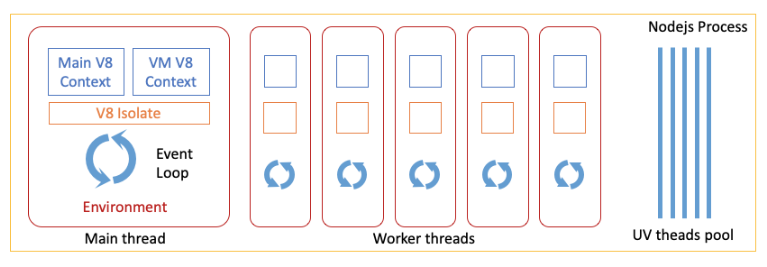
The design of Aworker adopts the model of single process and single thread, that is, the worker thread in the above model is separately extracted and put into an independent process. Worker can therefore support fork, so as to avoid the startup consumption from main() and achieve the purpose of fast startup.
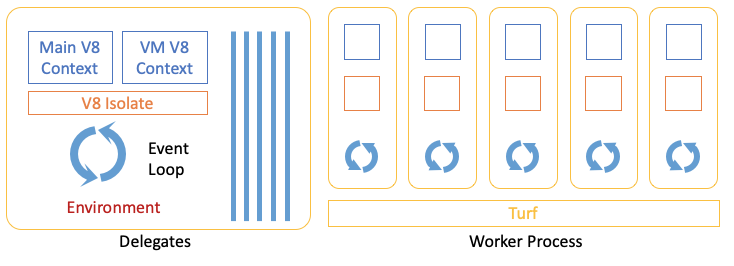
In order to support single thread, Aworker has also made the following modifications:
- Use the Linux AIO feature to replace the synchronous file system operations in libuv (not POSIX AIO, the two are different. Posix AIO is similar to the existing implementation of libuv );
- Use V8's SingleThread mode, which is a capability implemented for Low-end devices, but is very consistent with the Serverless resource model;
And in order to manage and isolate these worker processes, we need a lightweight business process container management component, Turf, which is used to create new Aworker service processes through WarmFork, and can provide a certain degree of resources and environment isolation capabilities, Also compatible with OCI. Different from traditional runc, rund containers, turf is designed to host such as Aworker This type of lightweight JS Runtime does not require image to run, has lower overhead, and can support higher deployment density.
Alinode WarmFork and Normal fork:
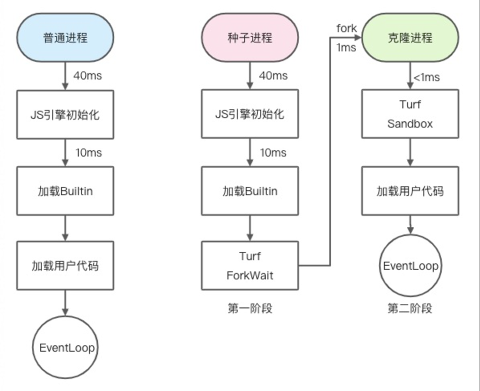
Provides a "copied" process, called a "seed process", and other service processes are clones of this process. For example, as a seed process, Aworker needs to determine a point in time at which it can be cloned, and uses its own state (memory) as the initial state of the cloned process.
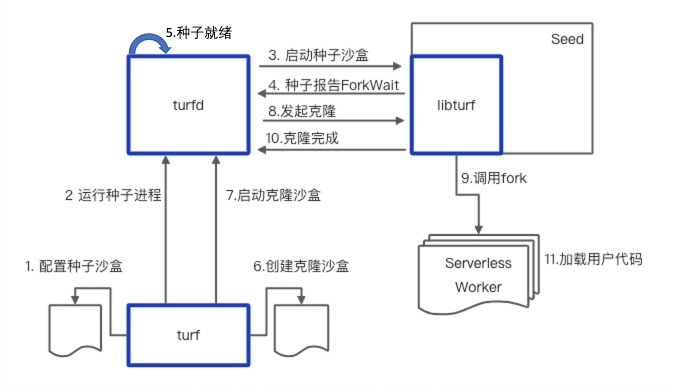
The system sequence diagram of WarmFork is as follows:
Startup Snapshot
WarmFork can solve the fast startup of the service process on a single machine, and the Startup Snapshot solution is required for cold startup. The difference between Startup Snapshot and CodeCache is that Startup Snapshot can save the logic execution state of user code, while CodeCache only saves code parsing results and still needs to be re-executed user code logic.
By design, Startup Snapshot can provide fast recovery with user code logic, but it also has limitations:
- The Startup Snapshot is sensitive to memory overhead. If a large amount of memory is used in the application startup phase, it may cause negative optimization;
- User code startup requires unambiguous states, such as IP address, date, connection status, service discovery results, etc. For these ambiguous contents, the user code needs to have the ability to correct when the process resumes;
V8's Startup Snapshot Serializer is an object traverser similar to GC. This traverser traverses the Root object added to the Snapshot, traverses its corresponding object graph and generates a series of deserialization instructions according to the object relationship.
Startup Snapshot is equivalent to starting from the V8 Context object and its globalThis, traversing all objects in the heap and serializing object relationships and references into unique bytecodes, forming a linear storable state. And when restoring, interpret and execute these bytecodes to restore the reference relationship between the contents of the objects in the heap and them.
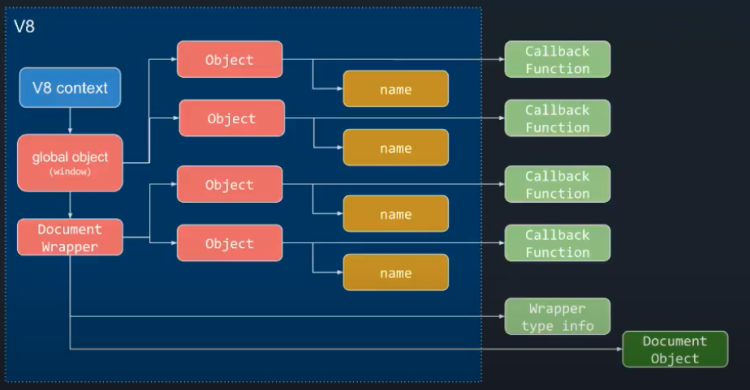
For the Startup Snapshot of the built-in runtime, Blink and Node.js have very significant acceleration effects:
- Blink can finally have 1.5-3 times the optimization effect;
- Node.js finally has 2-5 times the optimization effect (100ms→20ms);